Hazardous Substance and Impurities in Water
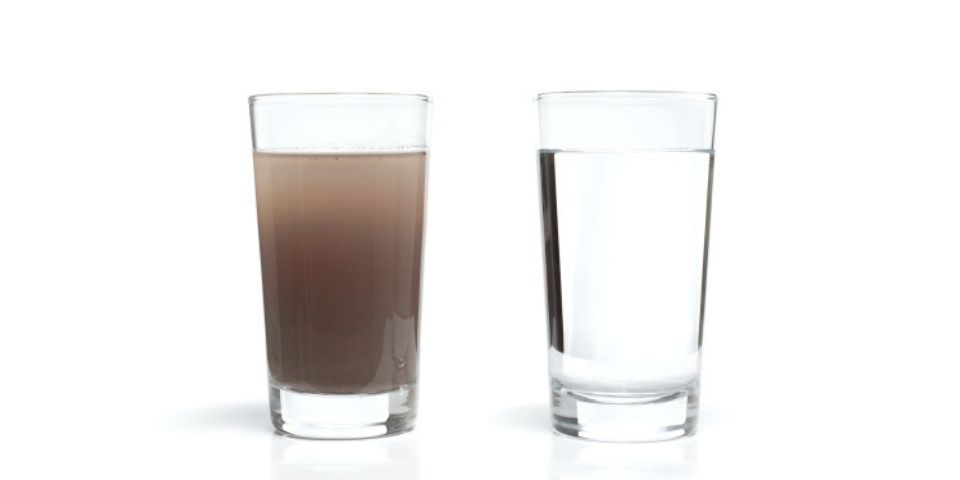
Water pollution occurs when harmful substances—often chemicals or microorganisms—contaminate a stream, river, lake, ocean, aquifer, or other body of water, degrading water quality and rendering it toxic to humans or the environment. According to the most recent surveys on national water quality from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, nearly half of our rivers and streams and more than one-third of our lakes are polluted and unfit for swimming, fishing, and drinking.
Types of Water Pollution
- Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. A unit of rock or an unconsolidated deposit is called an aquifer when it can yield a usable quantity of water. one of our least visible but most important natural resources. Nearly 40 percent of Americans rely on groundwater, pumped to the earth’s surface, for drinking water. For some folks in rural areas, it’s their only freshwater source. Groundwater gets polluted when contaminants—from pesticides and fertilizers to waste leached from landfills and septic systems—make their way into an aquifer, rendering it unsafe for human use. Ridding groundwater of contaminants can be difficult to impossible, as well as costly. Groundwater can also spread contamination far from the original polluting source as it seeps into streams, lakes, and oceans.
- Surface water is water located on top of the Earth's surface, and may also be referred to as blue water. In common usage, it is usually used specifically for terrestrial waterbodies, the vast majority of which is produced by precipitation and runoff from nearby higher areas. According to the most recent surveys on national water quality from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, nearly half of our rivers and streams and more than one-third of our lakes are polluted and unfit for swimming, fishing, and drinking. Nutrient pollution, which includes nitrates and phosphates, is the leading type of contamination in these freshwater sources. While plants and animals need these nutrients to grow, they have become a major pollutant due to farm waste and fertilizer runoff. Municipal and industrial waste discharges contribute their fair share of toxins as well. There’s also all the random junk that industry and individuals dump directly into waterways.
The Most Common Type of Water Contaminants
Microbial contamination The contamination of drinking water by pathogens causing diarrhoeal disease is the most important aspect of drinking water quality. The problem arises as a consequence of contamination of water by faecal matter, particularly human faecal matter, containing pathogenic organisms.
Physical contaminants primarily impact the physical appearance or other physical properties of water. Examples of physical contaminants are sediment or organic material suspended in the water of lakes, rivers and streams from soil erosion.
Chemical contaminants are elements or compounds. These contaminants may be naturally occurring or man-made. there are many sources of chemical contaminants in drinking water. However, the most important contaminants from a health standpoint are naturally occurring chemicals that are usually found in groundwater. Examples of chemical contaminants include nitrogen, bleach, salts, pesticides, metals, toxins produced by bacteria, and human or animal drugs.
- Arsenic : Waterborne arsenic is a major cause of disease in many parts of the world including the Indian sub-continent—particularly Bangladesh and Bengal—South America, and the Far East. It is the only contaminant that has been shown to be the cause of human cancers following exposure through drinking water. Besides cancer of the skin, lung and bladder and probably liver, arsenic is responsible for a range of adverse effects, including hyperkeratosis and peripheral vascular disease. In Bangladesh, where millions of tube wells were sunk, the concentration of arsenic can vary significantly between wells only a short distance apart.
- Fluoride : Waterborne fluoride is another major cause of morbidity in a number of parts of the world, including the Indian sub-continent, Africa and the Far East, where concentrations of fluoride can exceed 10 mg/l. High intakes of fluoride can give rise to dental fluorosis, an unsightly brown mottling of teeth, but higher intakes result in skeletal fluorosis, a condition arising from increasing bone density and which can eventually lead to fractures and crippling skeletal deformity. Many factors appear to influence the risk of such adverse effects, including volume of drinking water, nutritional status and, particularly, fluoride intake from other sources.
- Mercury is a liquid metal that can be found in various natural deposits. Erosion of natural deposits, discharge from refineries & factories, landfill runoff and cropland runoff are just a few of the ways that mercury can get into public drinking water. Being exposed to high levels of mercury over time can cause kidney damage.
- Iron and manganese : Both iron and manganese can occur at high concentrations in some source waters that are anaerobic14. When the water is aerated they are oxidized to oxides that are of low solubility. These will cause significant discolouration and turbidity at concentrations well below those of any concern for health.
- Agricultural chemicals : Agriculture is another source of chemical contamination. In this case the most important contaminant is nitrate, which can cause methaemoglobinaemia, or blue-baby syndrome, in bottle-fed infants under 3 months of age.
- Herbicides enter the drinking water system by accumulation in public soil and water sources. Most commonly, they enter the water system from rainfall and irrigation which wash herbicides off farmlands and into lakes and rivers. Atrazine, a herbicide commonly used on golf courses, can interfere with the bodies hormonal activity and reproductive organs.
- Bentazon: Short exposures to bentazon at levels much higher than the MDH guidance value are associated with developmental effects, including fetal death. Longer exposure at levels above the current guidance value are associated with anemia and other blood system effects. Bentazon has been shown to change the size of thyroid glands in animals, an indication that it might be altering thyroid function.
- Benzo[a]pyrene: Exposure to BaP has the potential to increase your risk of certain types of cancer, including in the digestive tract and liver for drinking water exposures based on laboratory studies.In addition to cancer, BaP causes brain development and activity changes in young animals exposed in the laboratory. Animal studies have also shown male and female reproductive system changes.
- Cadmium: Low level exposure to cadmium decreases bone density and disrupts bone composition. Rapidly growing bones are the most sensitive to these effects, so children are at an increased risk. C admium does not easily leave our bodies and tends to build up in the kidney. As a result, both shorter, higher exposures and lifetime low level exposures to cadmium can cause kidney disease in older adults. Although cadmium can cause cancer when inhaled, there is little evidence to support that it can cause cancer when ingested.
- Chloroform: Animal studies indicate that short exposures could be associated with suppression of the immune system, increased liver weight and liver lesions, incomplete skull formation and decreased body weight gain in pups. Additionally, longer exposures in laboratory animals at levels above the guidance value are associated with effects to male reproductive organs as well.
- Lead: Coming in contact with lead can cause serious health problems for everyone. There is no safe level of lead. Babies, children under six years, and pregnant women are at the highest risk. Coming in contact with too much lead can damage the brain, kidneys, and nervous system. In children, lead can also slow development or cause learning, behavior, and hearing problems.
- Chlorine is a powerful oxidant added to the water by several municipal water systems to control microbes. Chlorine can be absorbed through physical consumption as well as through your skin while bathing. Chlorine can severely dry skin and hair and cause irritating effects to your eyes and nose.
Biological contaminants are organisms in water. They are also referred to as microbes or microbiological contaminants. Examples of biological or microbial contaminants include bacteria, viruses, protozoa, and parasites.
Radiological contaminants are chemical elements with an unbalanced number of protons and neutrons resulting in unstable atoms that can emit ionizing radiation. Examples of radiological contaminants include cesium, plutonium and uranium.
- Selenium and uranium : Selenium and uranium have also both been shown to cause adverse effects in humans through drinking water. In seleniferous areas, drinking water can contribute to high selenium intakes, which can give rise to loss of hair, weakened nails and skin lesions, and more seriously, changes in peripheral nerves and decreased prothrombin time. Uranium is found in groundwater associated with granitic rocks and other mineral deposits. It is a kidney toxin and has been associated with an increase in fractional calcium excretion and increased microglobulinurea, although within the normal range found in the population.
Urban pollution : Industry and human dwellings are also a source of potential contaminants. The most common are heavy metals, and solvents, such as tri and tetrachloroethene, which are sometimes found in groundwater and hydrocarbons, particularly from petroleum oils. There is little good evidence that these pollutants occur at concentrations in drinking water that are sufficient to cause health effects, but some of the low molecular weight aromatic hydrocarbons can give rise to severe odour problems in drinking water at concentrations of less than 30 μg/l.
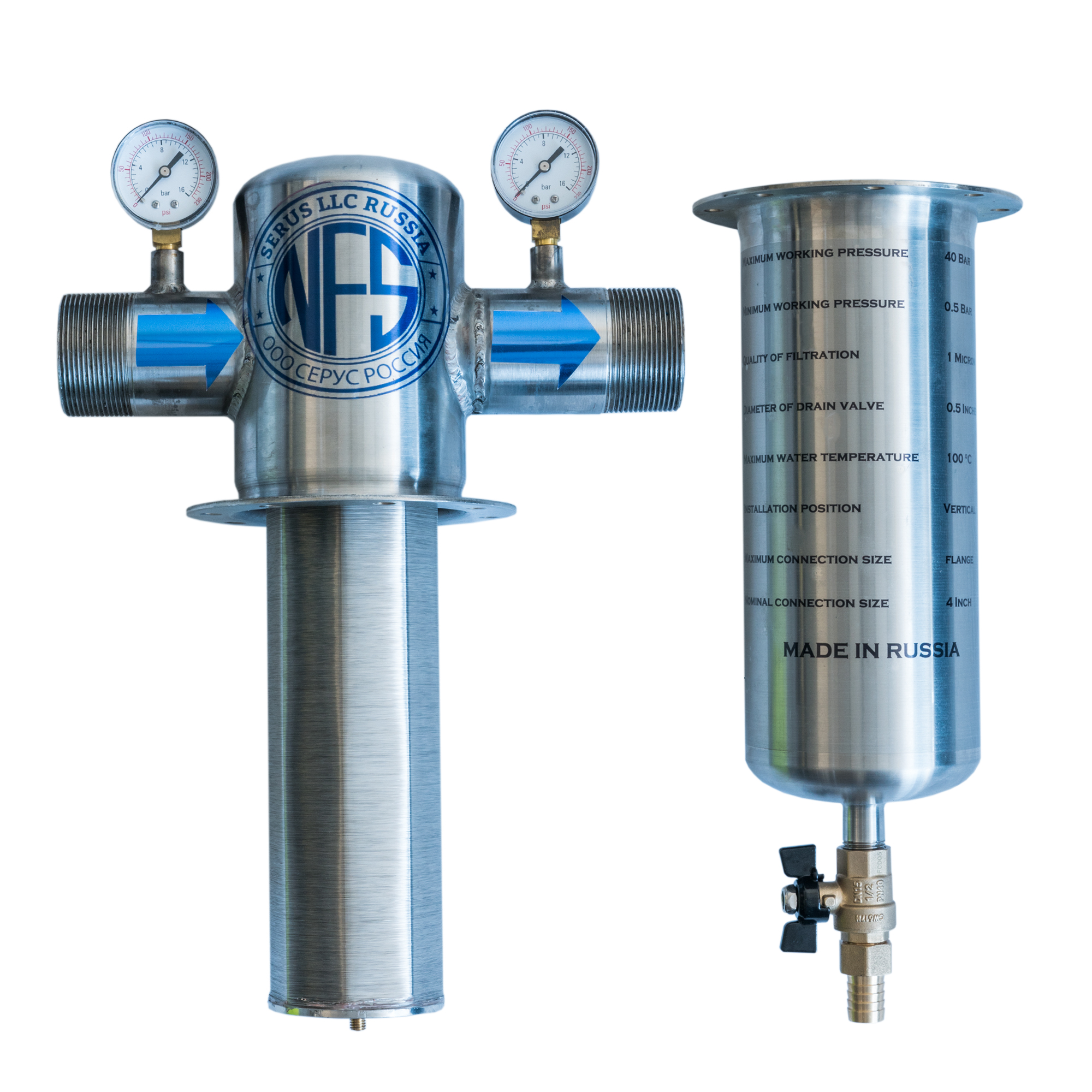
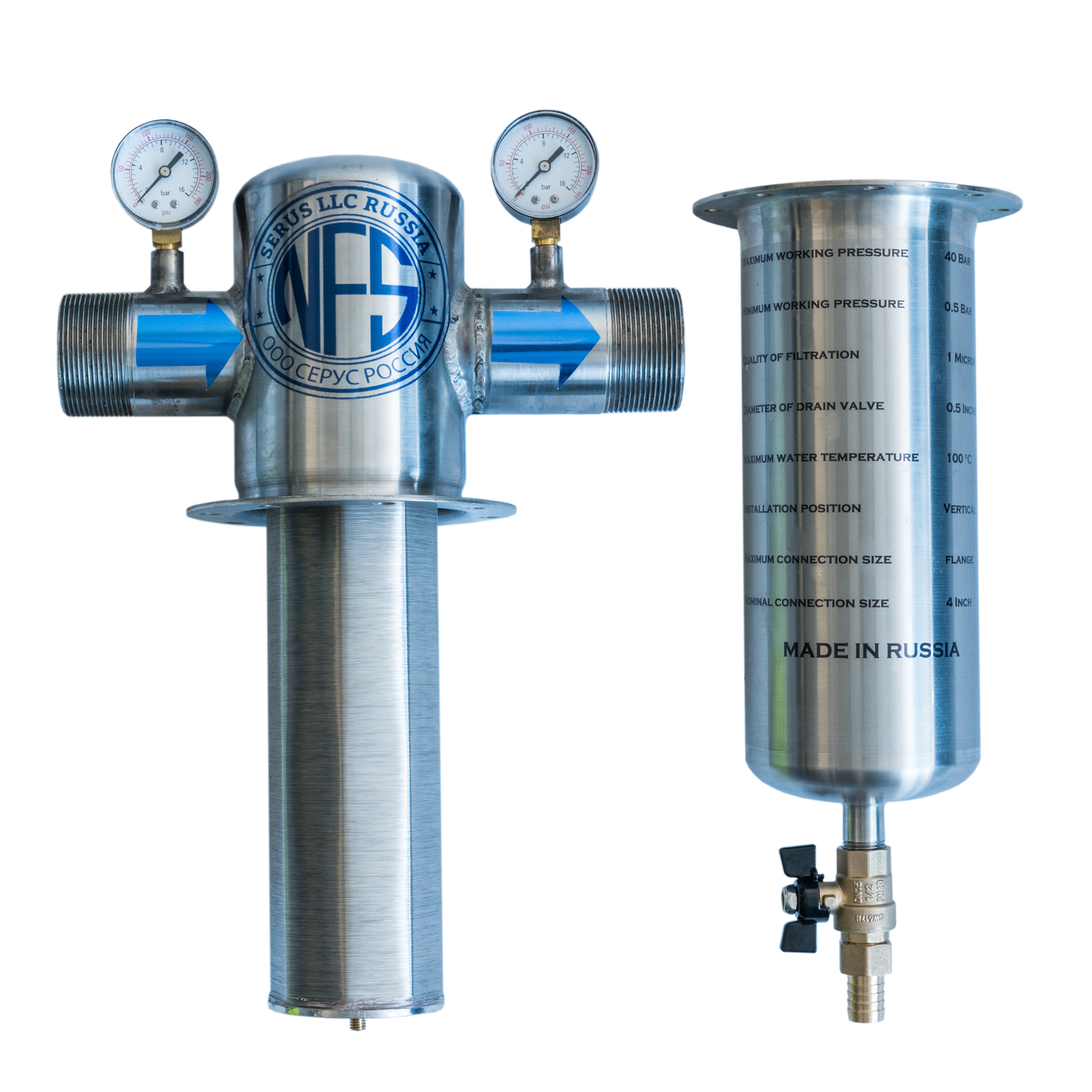
H2X Global is a leading provider of water filtration systems. We have a variety of Water Filtration System to meet the most demanding water treatment needs, which is used in different areas include - Residential Water Filtration, Industrial Water Filtration, Commercial Water Filtration & Purification, and Agricultural Water Filtration. We Use Revolutionary Russian Nanofiltration Technology, In it Nanofiltration membranes are utilized for the filtration of water with low total dissolved solids (TDS) for the purposes of eradicating organic substances and softening water. Nanofiltration is usable in many water and wastewater treatment industries for the practical removal of ions and organic material.
Nano Filters has been involved in numerous technical concerns, especially elimination of biological and organic toxins and impurities. Furthermore, some contaminants and toxins such as binding metal ions and 4-nitrophenol in water solution can be decomposed by Nano Filters.
Call & Whatsapp For Direct Enquiry:
+1 760.608.3534
Water Filter Price List
Email: water@h2oxglobal.com